Diamond Color

Key points about diamond color:
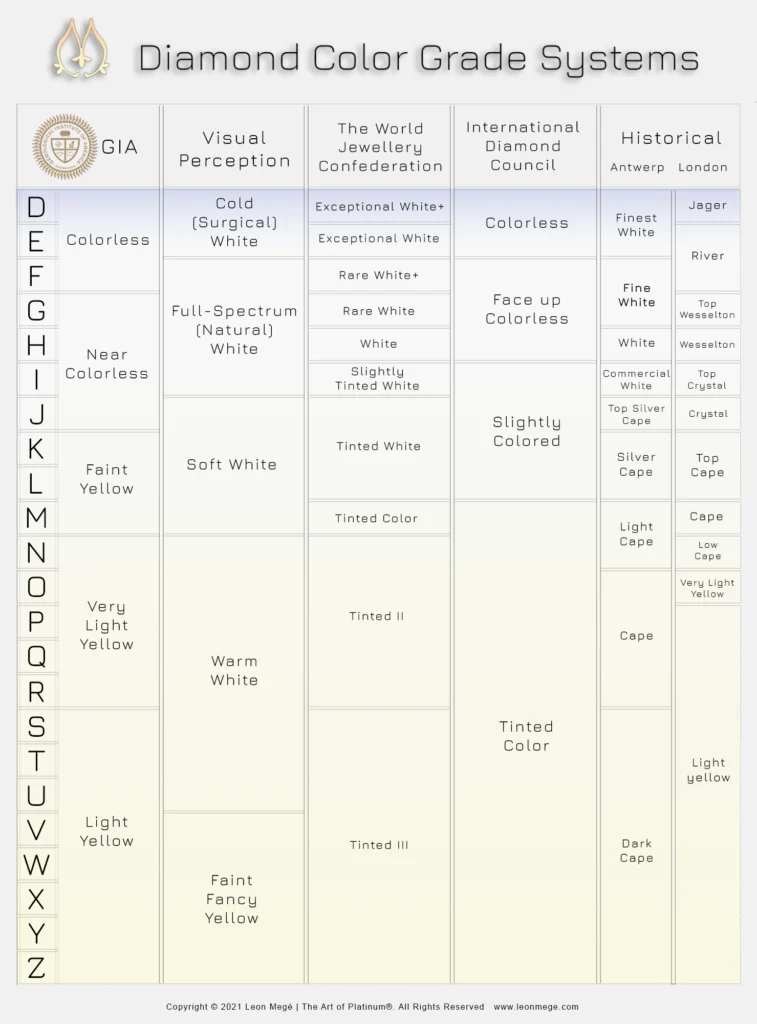
Colorless (D-F): Diamonds in the D to F range are considered colorless and are highly desirable because they allow the most light to pass through, maximizing their brilliance and sparkle. These diamonds appear white or colorless to the naked eye, and any differences in color are typically only visible under controlled lighting conditions.
Near Colorless (G-J): Diamonds in the G to J range are classified as near colorless. While they may exhibit slight traces of color when compared to colorless diamonds, these differences are often difficult to detect without direct comparison. Near colorless diamonds offer excellent value, as they can appear nearly colorless to the naked eye while being less expensive than higher-grade diamonds.
Faint Yellow (K-M): Diamonds in the K to M range have a faint yellow tint that becomes more noticeable as you move down the color scale. While these diamonds may appear slightly yellowish, especially when viewed from the side, they can still exhibit good brilliance and sparkle. Faint yellow diamonds are often more affordable than higher-grade stones and can be a budget-friendly option for those seeking larger carat weights.
Very Light Yellow (N-R): Diamonds in the N to R range have a very light yellow or brown tint that is more pronounced than faint yellow diamonds. While these diamonds may not be as colorless as higher-grade stones, they can still exhibit attractive sparkle and beauty, particularly when well-cut. Very light yellow diamonds are typically less expensive than higher-grade stones and may appeal to buyers seeking value.
Light Yellow to Light Brown (S-Z): Diamonds in the S to Z range exhibit noticeable yellow or brown tinting and are considered lower in color quality. While these diamonds may still possess desirable qualities such as good cut, clarity, and carat weight, their color may significantly impact their appearance and value. Light yellow to light brown diamonds are generally less expensive than higher-grade stones and may be suitable for buyers with budget constraints.
It’s important to note that diamond color is typically assessed with the diamond face-down against a white background under controlled lighting conditions. The goal is to evaluate the body color of the diamond, excluding any surface reflections or environmental factors. Additionally, diamond color can interact with other factors such as cut and clarity, so it’s essential to consider the overall quality of the diamond when making a purchase decision.
Diamond color refers to the presence or absence of color in a diamond. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and other gemological laboratories use a grading scale to assess diamond color, ranging from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). The color grade is determined by comparing the diamond to a set of master stones under controlled lighting
Even though many of these color differences in diamonds are so little that the untrained eye cannot see them, they have a significant impact on both the quality and cost of the stone. Therefore, in order to determine which hue is appropriate for your diamond, it is crucial to consult a Lab expert.